Sleep apnea affects millions of people worldwide, yet many remain unaware of its far-reaching health consequences.
Beyond the apparent symptoms of snoring and disrupted sleep, this condition may play a significant role in unwanted weight gain.
The relationship between sleep disorders and metabolism is complex, involving hormonal changes, behavioral shifts, and physiological disruptions that create perfect conditions for weight accumulation.
Understanding this connection is crucial for anyone struggling with both sleep issues and weight management, as addressing one condition often helps improve the other.
This guide examines the scientific mechanisms linking sleep apnea to weight gain and offers actionable strategies for overcoming this complex cycle.
Does Sleep Apnea Really Make You Gain Weight?
Yes, sleep apnea can make you gain weight.
Sleep apnea is a severe sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, affecting over 22 million Americans.
The condition manifests in three primary forms: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), when throat muscles relax and block the airway; central sleep apnea, where the brain fails to send proper breathing signals; and complex sleep apnea syndrome, which combines both types.
Common symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, morning headaches, and excessive daytime sleepiness.
These sleep disturbances create a cascade of physiological changes that directly contribute to weight gain through hormonal imbalances and metabolic disruption.
How Sleep Apnea Contributes to Weight Gain

Sleep apnea creates a complex web of physiological and behavioral changes that work together to promote weight gain. The condition disrupts your body’s natural processes on multiple levels.
Understanding these mechanisms helps explain why people with sleep apnea often struggle with weight management despite their best efforts.
The Physiological Factors: How Sleep Apnea Affects the Body
Sleep apnea triggers several metabolic disruptions that promote weight gain through complex biological mechanisms.
When sleep is fragmented, your body produces stress hormones like cortisol at inappropriate times, with raised levels promoting fat storage, particularly around the midsection.
Sleep deprivation affects two key hunger hormones: leptin (the “fullness” hormone) decreases, reducing feelings of satiety, while ghrelin (the “hunger” hormone) increases, stimulating appetite even when you don’t need food.
Interrupted sleep patterns disrupt circadian rhythms that regulate metabolism, potentially slowing metabolic rate by up to 20%.
The repeated oxygen drops during apnea episodes trigger inflammatory responses and additional stress hormone release, further contributing to metabolic dysfunction and stubborn weight gain.
Behavioral Factors: How Sleep Apnea Leads to Weight Gain
Beyond physiological changes, sleep apnea creates behavioral patterns that significantly promote weight gain through lifestyle disruptions.
Chronic fatigue from poor sleep quality makes exercise feel overwhelming, with many patients reporting difficulty maintaining regular workout routines, a preference for sedentary activities, and reduced energy for daily physical tasks.
Sleep deprivation affects decision-making areas of the brain, leading to increased cravings for high-calorie processed foods, poor portion control, late-night eating habits, and reliance on caffeine and sugar for energy.
The stress and mood changes associated with chronic sleep loss often trigger emotional eating behaviors, creating additional barriers to weight management and establishing unhealthy coping mechanisms that persist even when sleep improves.
Health Risks and Impact of Untreated Sleep Apnea
Untreated sleep apnea creates serious health consequences beyond weight gain and poor sleep.
- Cardiovascular risks include 140% higher stroke risk and 130% increased heart attack risk. The condition causes high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, and potential heart failure.
- Metabolic problems develop as diabetes risk increases by 250%. Blood sugar control becomes difficult due to insulin resistance and increased inflammation.
- Cognitive and safety issues include memory problems, concentration difficulties, and a 2-3 3-times higher accident risk due to daytime sleepiness.
- Mental health suffers as chronic sleep loss contributes to depression and anxiety disorders.
Can Weight Loss Cure Sleep Apnea?
Weight loss can significantly improve or even eliminate sleep apnea symptoms. Losing just 10% of body weight reduces sleep apnea severity by 25-30%.
For mild cases, losing 20-30 pounds may completely resolve the condition by reducing tissue around the neck and throat that blocks breathing.
However, results depend on severity, anatomy, and underlying causes. Some patients still need CPAP therapy after weight loss.
Combining weight loss with medical treatment produces the best outcomes, and maintaining weight loss long-term is essential to prevent symptom return.
Practical Tips to Manage Sleep Apnea and Weight


Effective management requires a comprehensive approach combining medical treatment with lifestyle modifications for optimal results.
Sleep Hygiene Improvements
Quality sleep habits form the foundation of successful sleep apnea management and can significantly improve symptoms. These changes help maintain natural sleep cycles and reduce airway obstruction during rest.
- Maintain consistent sleep and wake times.
- Create a comfortable, dark sleeping environment.
- Avoid alcohol and heavy meals before bedtime
- Sleep on your side to reduce airway obstruction
Lifestyle Modifications
Daily lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing both sleep apnea and weight-related challenges. These modifications support overall health while specifically targeting factors that worsen sleep disorders.
- Start with a gentle, sustainable exercise routine.s
- Emphasize whole foods and balanced nutrition
- Practice stress management techniques
- Stay adequately hydrated throughout the day
Medical Management
Professional medical care ensures proper treatment and monitoring of your sleep apnea condition. Working with healthcare providers allows for personalized treatment plans that address your specific needs.
- Use prescribed CPAP or oral appliance therapy consistently
- Work closely with healthcare providers to monitor progress
- Consider specialized weight loss programs designed specifically for people with sleep disorders to address both conditions effectively
The Vicious Cycle: Sleep Apnea and Obesity
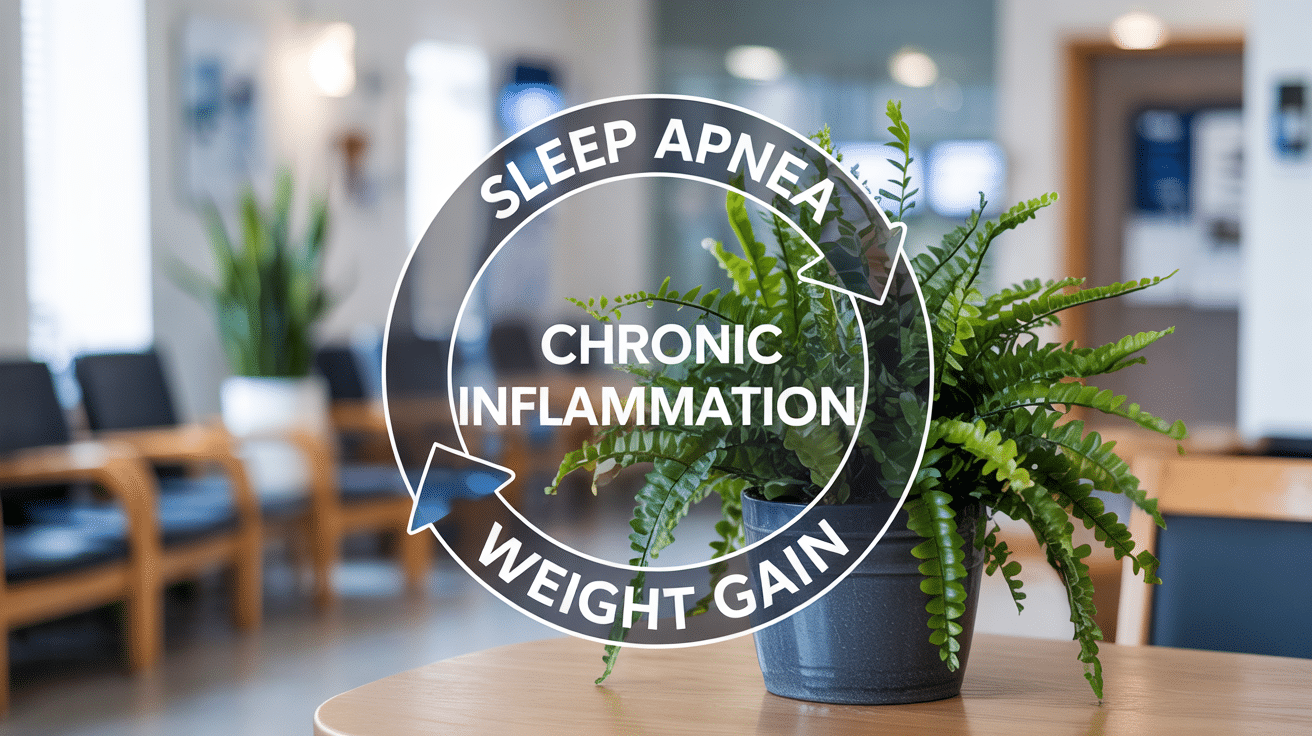

Sleep apnea and weight gain create a self-perpetuating cycle that becomes increasingly difficult to break without intervention.
Weight gain worsens sleep apnea because extra weight, especially around the neck and throat, increases airway obstruction during sleep.
Both conditions contribute to chronic inflammation, further disrupting normal metabolism and making weight loss more challenging.
Breaking this cycle requires addressing both sleep apnea and weight management simultaneously for optimal health outcomes and sustainable improvements.
Weight Management Strategies for Sleep Apnea Patients
Targeted strategies help sleep apnea patients overcome unique weight loss challenges while improving sleep quality simultaneously. Regular meal timing stabilizes blood sugar and energy levels.
| Strategy | Benefits | Implementation Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Gradual calorie reduction | Sustainable weight loss without energy crashes | Reduce daily intake by 300-500 calories |
| Regular meal timing | Stabilizes blood sugar and energy levels | Eat every 3-4 hours during waking hours |
| Protein-rich breakfast | Reduces afternoon cravings | Include 20-30g of protein in the morning meal |
| Evening exercise | Improves sleep quality | Light activity 2-3 hours before bed |
Pro Tip: Track your sleep quality alongside your weight loss progress using a sleep diary or smartphone app. Recording both metrics helps you identify which dietary and exercise changes most effectively improve your sleep.
Take Action for Better Health
The relationship between sleep apnea and weight gain involves complex physiological and behavioral factors that create significant barriers to weight management.
Hormonal imbalances, including disrupted leptin and ghrelin levels, combined with metabolic slowdown and increased cortisol production, establish biological conditions favoring weight accumulation.
Behavioral changes such as reduced physical activity, poor food choices, and emotional eating patterns further compound the problem. However, understanding this connection provides hope for effective treatment.
Taking proactive steps towards treatment can help improve both your sleep and your weight management efforts. Share your experiences or ask questions in the comments below – we’re here to help!














